In this post, Dr Richard Nicholls discusses how frontline employees (FLEs) can offer valuable insights into situations where customers interact with the other customers around them during the consumption of a service. This area of research, usually known as customer-to-customer interaction (CCI) or C2C interaction, has predominantly been investigate from a customer perspective but there are clear advantages to also gaining an employee perspective.
It has long been realised that as services are produced and consumed, that the customer is often ‘in the factory’. This makes managing services very different from managing manufacturing. There has been a vast amount of research on how employees and customers interact with one another (Subramony et al., 2021). But since the 1970s academics have become increasingly aware that customers also interact with each other, and this can influence how a service is experienced (Heinonen & Nicholls, 2022). This field is usually referred to conceptually as customer-to-customer interaction (CCI) or as customer-to-customer (C2C). Examples of CCI include a noisy passenger on a train, another shopper being extremely slow at the checkout, or, on a positive note, another customer providing some useful information.
The emergence of CCI and its focus on the customer’s perspective
There was relatively little published on CCI until a landmark article by Martin and Pranter (1989) spawned some significant pioneer publications in the 1990s (e.g., Baron, Harris, & Davies, 1996; Grove & Fisk, 1997). Developments such as the growth of the internet, the expansion of self-service technology and the growing interest in relationship marketing, served to fuel research interest in C2C in the noughties. Indeed, by the end of that decade it was considered that “the study of CCI has now joined the mainstream of service management research” (Nicholls, 2010, p. 94). Indeed, the same article, entitled ‘New directions for customer-to-customer interaction research’, catalysed further research into CCI (Colm et al., 2017; Nguyen & Menezes, 2021). Today, research into CCI has addressed a wide range of topics, including: the conceptualisation of CCI; the contexts that are associated with CCI; types of CCI; customer similarity and CCI; CCI and blame attribution; and the management of CCI (Nicholls, 2024).
When reviewing the CCI literature it becomes clear that most empirical studies are based on examining the customer perspective on CCI. These empirical studies take different approaches: some observe customers as they consume in service settings; some ask customers (on exit from the service setting) to recall any CCI experienced during the visit; some ask a sample to recall a memorable past incident of CCI, and so on. But ultimately, most studies describe CCI from a customer or customer-like perspective rather than through the eyes of the employee. This blog piece will focus on employees and CCI.
Frontline employees (FLEs) and CCI

The frontline employee is mentioned in the CCI literature. Indeed, over the last three decades the role of the FLE in managing CCI has received regular mention (Nicholls, 2024). In particular, the FLE service recovery role following C2C service failure has been highlighted (e.g., McQuilken et al., 2017). Likewise, some authors have discussed the views of customers on FLE responses to CCI (e.g., Hoffman & Lee, 2014). A few authors have pointed out that the FLE can be a contributor to negative CCI (e.g., Dorsey et al., 2016). However, although the FLE is frequently mentioned in the CCI literature (although often superficially), rarely has CCI been examined from the FLE perspective. Issues such as how perceptive FLEs are of CCI, or how they feel when dealing with CCI, have received extremely limited research attention (Nicholls & Gad Mohsen, 2019).
Nicholls and Gad Mohsen (2019) argue for the merits of seeking an employee perspective and present their research into CCI at a major library. The aim was to ground the investigation in employees’ experiences, using in-depth interviews with FLEs, to understand how employees notice, process and respond to CCI. The paper provides several findings that improve awareness of the value and nature of FLE insights into CCI. The study showed that employees could provide CCI insights that customers could not. It also revealed that employees could experience stress from managing C2C interaction and that the unpredictability surrounding customer reactions to employee intervention could be a major source of FLE stress. Furthermore, the study established that C2C interactions often took the form of triads, involving the FLE and two customer parties, and, as such, the study significantly extended understanding of the scope of triadic interactions.
Improving understanding of the FLE perspective on CCI
Far more needs to be understood about the FLE perspective on CCI. Two major areas for future research are (a) acquiring FLE insights to improve understanding of CCI and its management, and (b) improving understanding of the impact of dealing with CCI on FLE wellbeing (Nicholls, 2024). Regarding the former, key research issues include how FLEs acquire skills in handing difficult CCI situations; the approaches service organisations use to prepare FLEs for handling CCI situations; and FLE views on the adequacy of their training to handle CCI situations. Regarding the latter, key research issues include the long- and short-term psychological consequences of dealing with challenging CCI situations; the strategies adopted by FLEs to cope with CCI-induced stress; and the differences and similarities between handling difficult employee-to-customer interactions and difficult C2C interactions. Furthermore, building on Nicholls and Gad Mohsen (2019), further research into the service context in which an employee is interacting with two separate customer parties simultaneously has the potential to open up a new research front in the field of triadic interactions.

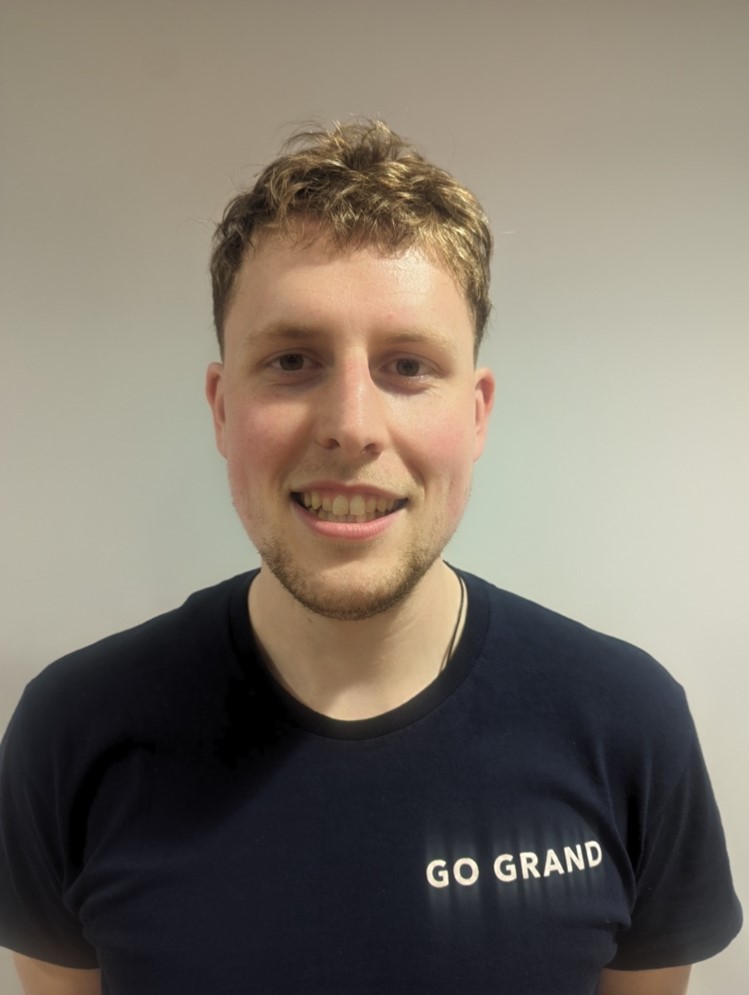
Dr Richard Nicholls
Richard is a Senior Lecturer in the Department of Marketing and Enterprise at Worcester Business School and the Customer Interactions Research Theme (CIRT) Lead. He is a member of the Interpersonal Relationships and Wellbeing Research Group. Richard has published extensively on customer-to-customer interaction (CCI) in leading service journals and in specialist academic research books.